Digital Transformation in Energy Market Report, Size, Overview, Trends & Analysis 2032
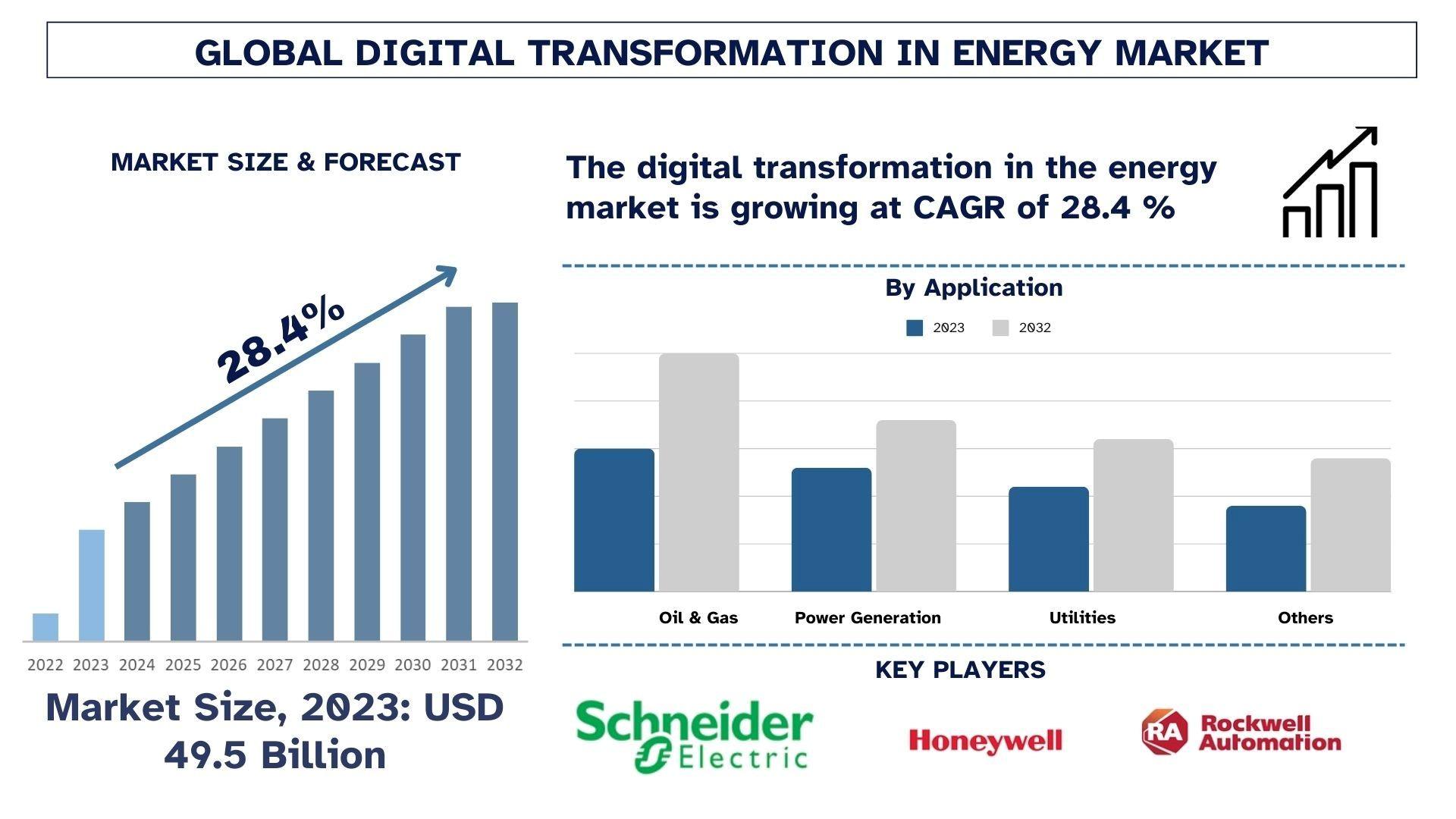
According to a new report by UnivDatos, the Digital Transformation in Energy Market is expected to reach USD Million by 2032 by growing at a CAGR of ~28.4%.
Introduction
New technology is changing the energy sector which has large physical assets and well-defined structures and practices. Digitalization is revolutionizing the way that energy is generated, marketed, and consumed in an organization and besides this, it has the following effects: Within the context of the transition to sustainable energy solutions, digital transformation is a key enabler of improvement of energy infrastructure and integration of renewable energy sources. The different areas of concern raised in this article include the demand drivers, the key applications associated with the digital transformation in the energy market and the costs incurred, the manufacturing map, and the trends expected in the future.
Demand
The following are some of the reasons that have led to the call for change in the energy sector: The desire to make processes in the energy industries more efficient, the integration of renewable energy sources, and the focus on sustainability. Energy firms continue to be under pressure to limit their carbon output and move to sustainable power generation and use where digital systems provide answers.
Moreover, the tendency to use microgrids and other distributed energy resources (DERs) also stimulates the need for digital transformation. These systems need elaborate digital monitoring, control, and management tools for the energy flow, so digitalization becomes mandatory for these systems.
Also, the complexity of the energy market with a combination of traditional and renewable sources of energy requires a high level of analysis and immediate data processing capabilities. Digital transformation empowers energy companies to make efficient decisions from the insights of the data, enhance the reliability of the grid, and interact more with customer needs by personalizing their services.
Applications
Digital transformation in the energy sector encompasses a wide range of applications, each contributing to the overall efficiency and sustainability of energy systems.
Smart Grids: One of the most significant applications of digital transformation in the energy sector is the development of smart grids. These grids leverage digital technologies such as advanced sensors, communication networks, and data analytics to monitor and manage energy distribution in real-time. Smart grids enable better integration of renewable energy sources, reduce energy losses, and enhance grid reliability.
Predictive Maintenance: Digital transformation allows energy companies to implement predictive maintenance strategies, which use data analytics and machine learning to predict equipment failures before they occur. This proactive approach reduces downtime, extends the lifespan of assets, and lowers maintenance costs.
Energy Management Systems (EMS): Energy management systems are another critical application of digital transformation. These systems use digital tools to optimize energy consumption in industrial, commercial, and residential settings. By analyzing real-time data, EMS can adjust energy usage based on demand, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Renewable Energy Integration: The integration of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, into the energy grid presents challenges related to intermittent and variability. Digital transformation enables the use of advanced forecasting models, energy storage solutions, and demand response strategies to manage these challenges effectively.
Customer Engagement Platforms: Digital transformation has also led to the development of customer engagement platforms that provide consumers with real-time information about their energy usage. These platforms empower consumers to make informed decisions, participate in demand response programs, and adopt energy-efficient practices.
Blockchain in Energy Trading: Blockchain technology is emerging as a key component of digital transformation in the energy market. It facilitates peer-to-peer energy trading, enhances transparency in energy transactions, and enables the creation of decentralized energy marketplaces.
Cost:
According to the particularities of the digital transformation process, the costs differ depending on the technologies and applications used in the energy sector. Thus, as much as digitalization is long-term advantageous in terms of saving costs and increasing efficiencies, the initial capital required is high.
The main expense is on the Direct Infrastructure for deploying smart meters sensors, and communication networks. These technologies are capital-intensive but are critical in supporting actionable data capture and processing in organizational contexts. Furthermore, the use of digital platforms and software solutions may require certain recurrent operational expenses such as licensing, additional maintenance, and cybersecurity among others.
Another issue of migrating to digital energy systems is raising the staff’s skills, which can also be costly. Businesses have to engage in education and training programs that enable the staff to gain new competencies so as to manage digital technology assets.
Still, the overall effect is usually positive and the return on investment (ROI) for digital transformation in the context of the energy sector is positive. The optimizations, savings, and improved capability in decision-making which are brought about by digital technologies are known to yield overall returns far beyond the investments needed.
Access sample report (including graphs, charts, and figures): https://univdatos.com/reports/digital-transformation-in-energy-market?popup=report-enquiry
Manufacturing
Manufacturing related to digital transformation in the energy sector can therefore be described as the development of complex manufacturing goods that are used to facilitate the reduction of digitalization within the energy sector. They are smart meters, sensors, communication networks, and the data analytical platform.
Thus, smart meters and sensors are vital for the further development of Smart Grids because the latter requires the gathering of real-time data. These devices are produced by firms that deal with precision engineering along with effective solutions in scale. A key constituent in smart metering whereby the act of production of these meters, has been growing due to factors such as government policies and the adaptation of smart grid technology.
Communication systems are the key components of digital energy systems; wired as well as wireless technologies are incorporated into them. These networks allow for data to be passed on from one part of the energy grid to another in a manner that is real-time and, thus can be controlled in real-time. Building of communication structure requires effort from energy providers, technology developers, and telecommunication industries.
On the software front, integrated data analytics platforms, energy management systems, and other smart technologies such as prediction of maintenance needs are some of the areas, that cannot be over-emphasized regarding digital transformation. Most of these platforms are created by specialized software firms experienced in big data, machine learning as well as artificial intelligence. In this context, it is necessary to connect these platforms with already existing power systems – it is one of the main steps in the digital revolution.
Conclusion
The global digital transformation in the energy market is reshaping how energy is produced, distributed, and consumed, leading to a more efficient, sustainable, and resilient energy system. While the initial costs of digitalization can be high, the long-term benefits in terms of operational efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced decision-making are substantial.
As the energy sector continues to evolve, driven by the need for sustainability and the integration of renewable energy sources, digital transformation will play an increasingly important role. The adoption of smart grids, predictive maintenance, energy management systems, and customer engagement platforms is expected to accelerate, leading to a more dynamic and interconnected energy market.
In conclusion, digital transformation is not just a trend but a necessity for the energy sector to meet the challenges of the 21st century. As technology continues to advance, the opportunities for innovation in the energy market will only grow, paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient energy future.
Report
Market Size, Trends, & Forecast by Revenue | 2024−2032.
Market Dynamics – Leading Trends, Growth Drivers, Restraints, and Investment Opportunities
Market Segmentation – A detailed analysis of technologies and applications.
Competitive Landscape – Top Key Vendors and Other Prominent Vendors
Contact Us:
UnivDatos
Contact Number - +1 978 733 0253
Email - contact@univdatos.com
Website - https://univdatos.com
Linkedin- https://www.linkedin.com/company/univ-datos-market-insight/mycompany
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Oyunlar
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



