What Are the Best Treatments for Angioedema?
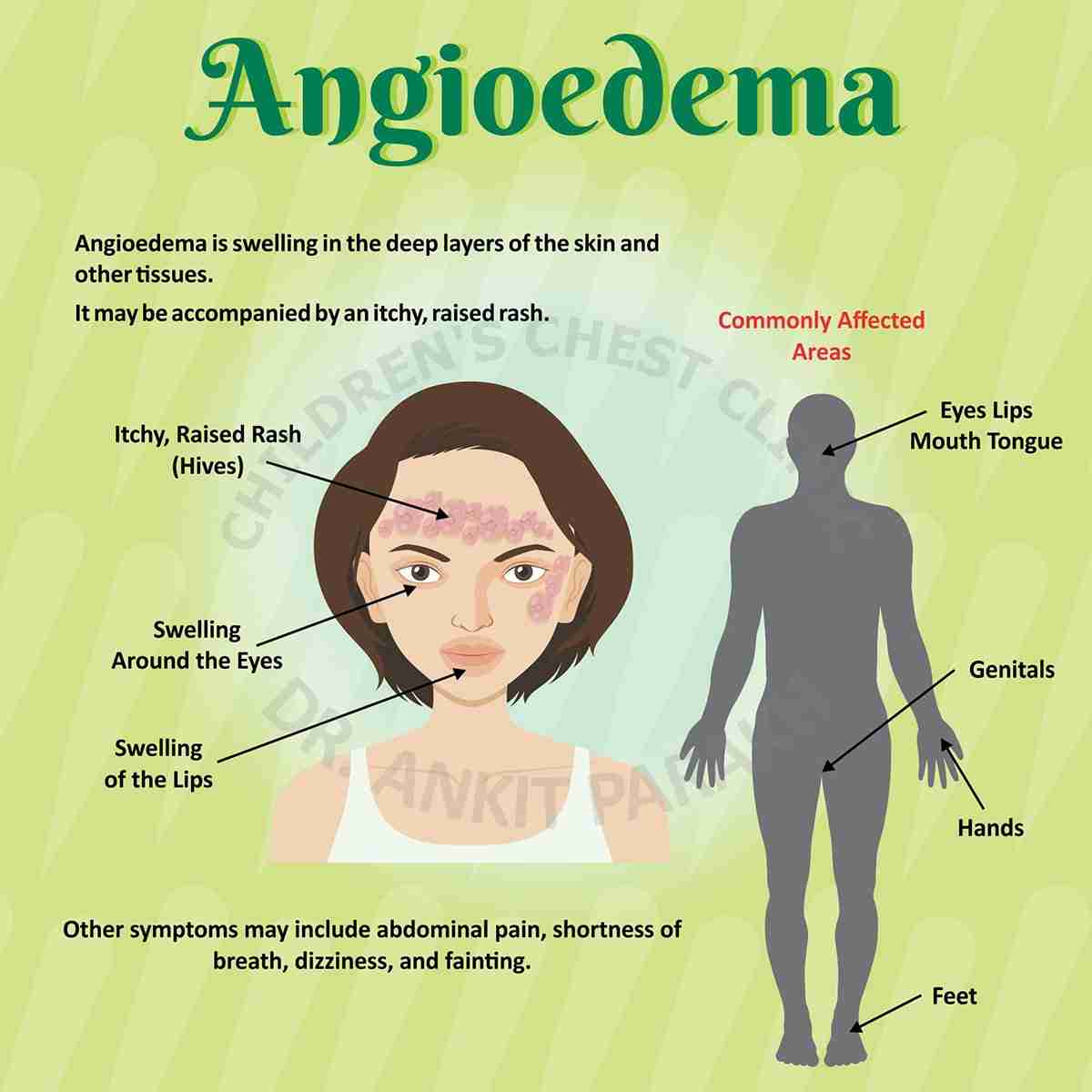
Angioedema is a medical condition characterized by sudden, localized swelling beneath the skin, often affecting areas like the face, lips, tongue, throat, or extremities. It can be triggered by allergic reactions, medications, genetic factors, or other underlying conditions. Effective treatment depends on the cause, severity, and whether it’s acute or chronic. Below, I’ll explore the best treatments for angioedema, incorporating the keyword "cephalexin wholesale" where relevant, while ensuring the information is comprehensive and practical.
Understanding Angioedema and Its Causes
Angioedema results from fluid leakage into deeper skin layers, often due to histamine release (in allergic or idiopathic cases) or bradykinin accumulation (in hereditary or ACE inhibitor-induced cases). Common triggers include:
- Allergic reactions: Foods (nuts, shellfish), insect stings, or medications.
- Medications: ACE inhibitors, NSAIDs, or antibiotics like cephalexin.
- Hereditary angioedema (HAE): Genetic mutations affecting C1 inhibitor protein.
- Acquired angioedema: Linked to autoimmune disorders or malignancies.
- Idiopathic angioedema: No identifiable cause.
Symptoms include swelling, redness, warmth, and sometimes pain. Severe cases affecting the throat can cause breathing difficulties, requiring urgent care. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, preventing recurrence, and addressing the underlying cause.
1. Antihistamines for Allergic Angioedema
For allergic angioedema, antihistamines are the first-line treatment. They block histamine, reducing swelling and itching. Non-sedating options like cetirizine (Zyrtec) or loratadine (Claritin) are preferred for daytime use, while diphenhydramine (Benadryl) may be used for rapid relief, though it causes drowsiness. Dosage typically ranges from 10–20 mg daily for cetirizine or loratadine, adjusted by a doctor based on severity.
In cases where angioedema is triggered by medications like cephalexin, a commonly used antibiotic, antihistamines can help manage mild reactions. The cephalexin wholesale purchases are often made by pharmacies to stock this antibiotic for infections, but patients must be monitored for side effects like angioedema. If cephalexin is the culprit, discontinuing it is critical, and antihistamines can stabilize symptoms while the body clears the drug.
For severe allergic angioedema, doctors may combine H1-blockers (like cetirizine) with H2-blockers (like ranitidine) to enhance histamine suppression. This approach is effective in 70–80% of acute cases, according to clinical studies.
2. Corticosteroids for Inflammation
Corticosteroids like prednisone or methylprednisolone are used when antihistamines alone aren’t enough, particularly in moderate to severe allergic angioedema. They reduce inflammation and swelling by suppressing the immune response. A typical regimen might involve 40–60 mg of prednisone daily for 3–5 days, tapered to avoid side effects.
For patients experiencing angioedema from antibiotics like cephalexin, corticosteroids may be prescribed alongside antihistamines. Cephalexin wholesale suppliers ensure availability for treating bacterial infections, but healthcare providers must weigh its benefits against risks like allergic reactions. Steroids are effective but not a long-term solution due to side effects like weight gain, high blood pressure, and immune suppression.
3. Epinephrine for Life-Threatening Cases
In emergencies, such as angioedema causing airway obstruction (anaphylaxis), epinephrine is the gold standard. Administered via auto-injector (EpiPen) or intramuscular injection (0.3–0.5 mg every 5-15 minutes as needed), it rapidly reduces swelling and restores breathing. Patients with a history of severe allergic reactions should carry an EpiPen, especially if exposed to triggers like foods or drugs, including cephalexin.
Cephalexin wholesale distributors supply this antibiotic to hospitals, where it’s used for infections like cellulitis. However, in rare cases, it triggers anaphylaxis or angioedema, necessitating epinephrine. Post-epinephrine, patients are monitored in a hospital, often receiving antihistamines and steroids to prevent recurrence.
4. Hereditary Angioedema (HAE) Treatments
HAE, caused by C1 inhibitor deficiency, doesn’t respond to antihistamines, steroids, or epinephrine because it’s bradykinin-mediated. Specialized treatments include:
- C1 inhibitor concentrates: Drugs like Berinert or Cinryze replace the deficient protein, reducing swelling within hours. Administered intravenously, they’re effective for acute attacks.
- Bradykinin receptor antagonists: Icatibant (Firazyr) blocks bradykinin, halting swelling. A single subcutaneous injection (30 mg) often resolves symptoms in 1–2 hours.
- Kallikrein inhibitors: Lanadelumab (Takhzyro) prevents bradykinin overproduction, used for long-term HAE prevention. Monthly injections reduce attack frequency by up to 87%, per clinical trials.
- Androgens: Danazol increases C1 inhibitor production but is less common due to side effects like liver toxicity.
For HAE patients, identifying triggers is key. While cephalexin isn’t a typical HAE trigger, infections treated with cephalexin (sourced from cephalexin wholesale markets) can stress the immune system, potentially worsening HAE symptoms. Doctors may adjust HAE therapies during such treatments.
5. Discontinuing Trigger Medications
For drug-induced angioedema, stopping the offending medication is essential. ACE inhibitors, linked to 20-40% of angioedema cases in emergency settings, are a common cause. Switching to alternatives like ARBs (losartan) reduces risk. Similarly, if cephalexin triggers angioedema, it’s discontinued, and alternatives like clindamycin are considered.
Cephalexin wholesale availability ensures it’s widely prescribed for infections, but patients with a history of drug allergies need careful monitoring. Doctors may perform skin tests or desensitization protocols if cephalexin is unavoidable, though this is rare for angioedema.
6. Supportive Care and Monitoring
Mild angioedema may resolve with cool compresses and avoiding irritants. Severe cases require hospital observation, especially if the throat or tongue is involved. Intubation or tracheostomy may be needed if airways are compromised. Patients are educated to avoid triggers, including medications like cephalexin, which is stocked via cephalexin wholesale channels for broad use.
7. Long-Term Management and Prevention
Preventing angioedema involves:
- Allergy testing: Identifying food or drug triggers, including antibiotics like cephalexin.
- Prophylactic medications: Antihistamines for idiopathic cases or HAE-specific drugs like lanadelumab.
- Patient education: Recognizing early symptoms and carrying emergency medications (EpiPen for allergic cases, icatibant for HAE).
For pharmacies, sourcing cephalexin wholesale ensures cost-effective access, but they must counsel patients on risks like angioedema. Electronic health records can flag patients with drug sensitivities, reducing recurrence.
Special Considerations
- Chronic idiopathic angioedema: May require long-term antihistamines or immunosuppressants like cyclosporine if resistant to standard treatments.
- Pregnancy: HAE treatments like C1 inhibitors are safe, but antihistamines and steroids are used cautiously. Cephalexin, often available through cephalexin wholesale, is generally safe in pregnancy but requires monitoring for allergic reactions.
- Pediatrics: Dosing adjustments are critical, and epinephrine remains safe for anaphylaxis.
Emerging Treatments
Research is exploring new bradykinin-targeted therapies for HAE and biologics like omalizumab (Xolair) for chronic idiopathic angioedema. Omalizumab, approved for urticaria, shows promise in reducing angioedema episodes by 70-90% in small studies. Gene therapies for HAE are also in trials, aiming to correct C1 inhibitor deficiencies permanently.
Conclusion
The best treatments for angioedema depend on its type and severity. Allergic cases respond to antihistamines, steroids, and epinephrine, while HAE requires specialized drugs like C1 inhibitors or icatibant. Discontinuing triggers, like ACE inhibitors or cephalexin, is crucial. Cephalexin wholesale ensures its availability for infections, but its rare link to angioedema highlights the need for vigilance. With proper diagnosis, acute management, and prevention strategies, most patients can manage angioedema effectively. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized treatment plans, especially if symptoms persist or worsen.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness

