Structural Factors Behind Heavy-Duty Plastic Trays
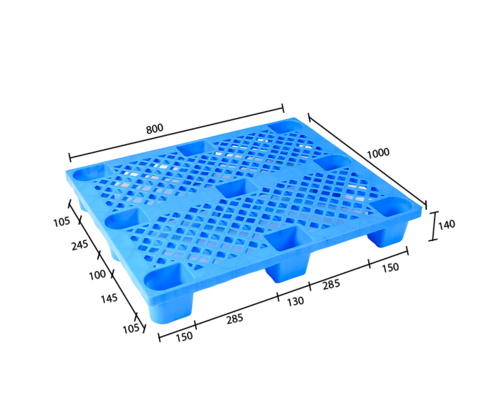
Understanding Load Capacity in Grid Plastic Trays
When evaluating industrial or logistics trays, load capacity is one of the most critical performance indicators. For products like the Single-Faced Grid Nine Feet Plastic Tray, users often focus on how structural details influence strength and durability. Among these details, grid depth and wall thickness play a decisive role in determining how much weight a tray can safely support without deformation or failure. Understanding these structural relationships helps buyers select trays that match their real-world operational needs.
Role of Grid Depth in Load Distribution
Grid depth refers to how deep each cell or rib extends below the tray’s top surface. Deeper grids increase vertical structural support by creating stronger load paths from the top surface down to the base. When weight is applied, deeper grid structures disperse stress more evenly across the tray, reducing pressure on any single point. This design minimizes sagging, especially when trays are used to carry dense or unevenly distributed loads over long periods.
Impact of Grid Thickness on Structural Strength
Thickness is equally important when analyzing tray performance. Thicker grid walls enhance resistance to bending and cracking under heavy loads. In high-load applications, thin grid structures may flex excessively, leading to fatigue over time. By contrast, thicker ribs maintain rigidity and allow the tray to perform consistently even under repeated stacking or transport cycles. This is particularly relevant for warehouse environments where trays are frequently moved by forklifts or conveyors.
Interaction Between Depth and Thickness
Grid depth and thickness do not operate independently; they work together to determine overall load-bearing capability. A tray with deep but thin grids may still fail under high stress, while a tray with thick but shallow grids may lack sufficient vertical support. Optimized designs balance both dimensions, ensuring that weight is transferred efficiently through the grid network to the tray’s nine-foot support points. This balance is a key reason why well-designed trays maintain shape and performance under demanding conditions.
Influence of the Nine-Feet Support Structure
The nine-foot base structure further amplifies the effects of grid depth and thickness. These support points act as anchors that channel load directly to the ground or pallet surface. When combined with appropriately deep and thick grid walls, the tray benefits from improved stability and reduced deflection. This structural synergy allows the tray to carry heavier loads while maintaining flatness and preventing warping during long-term storage.
Material Behavior Under Load Stress
Even with optimal grid geometry, material behavior plays a role in how depth and thickness affect load capacity. Plastic materials respond to stress through elastic deformation, meaning they can flex slightly and recover their shape. Adequate grid thickness helps control this flexing, while sufficient depth prevents excessive downward displacement. As a result, the tray can sustain static and dynamic loads without permanent deformation, extending its usable lifespan.
Practical Implications for Industrial Use
In practical applications, such as logistics, manufacturing, or agricultural storage, users often select a Single-Faced Grid Nine Feet Plastic Tray based on expected load conditions. Trays with deeper and thicker grids are better suited for heavy components, stacked goods, or long-term storage. Lighter-duty trays with shallower grids may suffice for short-term transport or low-density items. Understanding these differences allows businesses to avoid overengineering or underestimating load requirements.
The grid depth and thickness of a Single-Faced Grid Nine Feet Plastic Tray have a direct and measurable impact on its load-bearing capacity. Deeper grids enhance load distribution, thicker walls improve rigidity, and the interaction between the two determines long-term performance. When paired with a nine-foot support structure, these design elements create a stable and reliable tray capable of meeting demanding industrial needs. Selecting the right combination of grid depth and thickness is therefore essential for ensuring safety, efficiency, and durability in real-world operations.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jocuri
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Alte
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



